Network
Overview
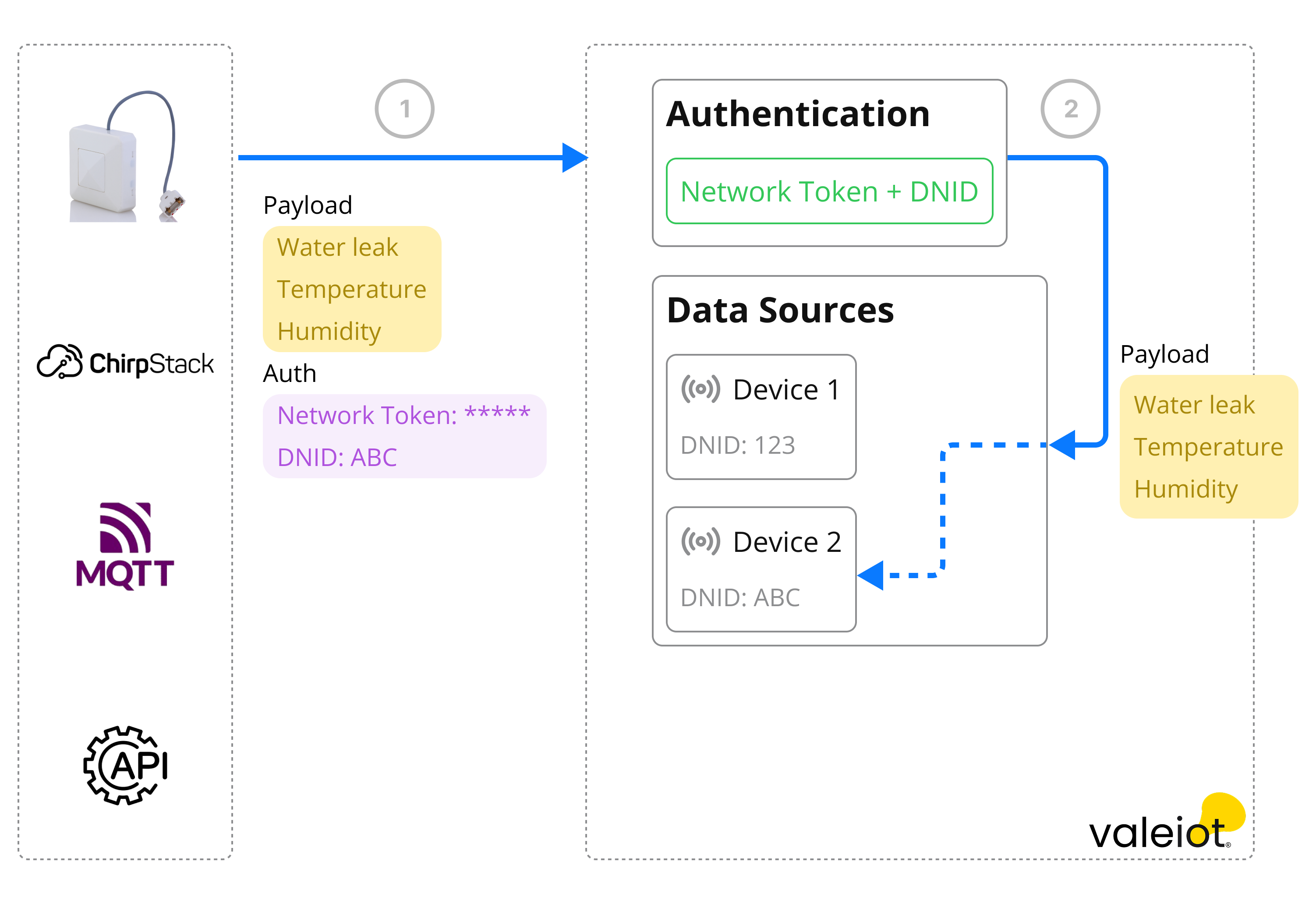
A Network serves as a logical gateway, providing access to a group of Data Sources. Its primary function is to authorize access and facilitate interaction.
The Network can be linked to a Data Source, granting access to it later. Each Network has unique Network Tokens, which are used to authorize requests.
When making a request using a Network Token to insert data into Valeiot, the system will validate the token and check if the DNID (Data Source Network Identification) corresponds to an existing Data Source linked to the Network. If both conditions are met, the data will be inserted successfully, as illustrated in the diagram below.
Note that the DNID serves as a unique identifier for the Data Source within the Network.
If your sensor or any external components do not send data in the Valeiot JSON format, you will need to use a Payload Parser. To learn more, read the section Payload Parser.
You’ll need to convert requests using a Middleware. Valeiot provides pre-built Middleware options, and we recommend checking the Middleware section to learn more.
An example of Network Token is:
us-east-1:Tjb9Iq8ATvNtmDlbp0RKtqQLToWUewMBjdvEbNAnMo17gR9xk60bjPVjXwBaDy.
It typically includes a server-identification prefix, like us-east-1, followed by a unique alphanumeric string.
Key Characteristics
- Data Source Access: A Network provides access to all Data Sources linked to it, allowing you to interact with them collectively.
- Network Token: Each Network has unique tokens which are used to authorize requests.
Use Cases
- Data Routing: Use the Network Token to send data to specific Data Sources linked to the Network, enabling scalability.
Sending Data Using Network Token
For detailed instructions on sending data to a Data Source using the Network Token, see the section Sending Data.